Climate Change and the Indian Economy - A Review
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.17.1.3
Copy the following to cite this article:
Sharma M, Singh R, Kathuria A. Climate Change and the Indian Economy - A Review. Curr World Environ 2022;17(1). DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.17.1.3
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Sharma M, Singh R, Kathuria A. Climate Change and the Indian Economy - A Review. Curr World Environ 2022;17(1). Available From:
Download article (pdf)
Citation Manager
Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 25-10-2021 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 14-03-2022 |
| Reviewed by: | 
 Alaeddine Zouari
Alaeddine Zouari
|
| Second Review by: |

 Sana Akhtar
Sana Akhtar
|
| Final Approval by: | Dr. Hemant Kumar |
Introduction
For a developing nation like India, climate change is a harsh reality. This is mostly because the backbone of the growth of a developing country is made of conventional methods of generating energy and resources. Despite a huge advancement in technologies, such countries often find themselves in conflicting positions.
Economy, development and climate change often cross each other’s paths resulting in increased risk and vulnerability. This can be understood from the precipitation requirements and rainfall. For example, owing to climate change, in many areas the groundwater level has plummeted. This is the outcome of more than ever concrete surfaces diminishing the recharge rate of aquifers.1 Indian agriculture rests on the support of groundwater and seasonal rainfall for the most part of the year. Consequently, the interplay of climate change and development factors has resulted in an acute water shortage for at least one month every year affecting a billion people in India while around 180 million suffer from severe water scarcity throughout the year.2
Latterly, climatic variations disguised as cyclones and floods have caused massive desolation of crops, property, and infrastructure. This has also caused negative impacts on human health, especially heat stressors. Rural dwellers continue to depend on agriculture for livelihood and food, making them explicitly vulnerable to climate variability and change. All these factors hitch socio-economic development goals.3,4
The national policies on climate change (“National Action Plan on Climate Change” (NAPCC)) are concentrated around human development and economic - industrial development policies. Local policies have helped in reducing urban air pollution levels. It is noteworthy that India is not responsible for rising temperatures despite contributing to 17.8% of the world’s population. It accounts for only 3.2% of cumulative emissions.5
However, a report prepared by Deloitte Economics Institute, entitled “India’s Turning Point: How climate action can drive our economic future” projects that if the current practices and policies continue then India, may lose US$6 trillion in current value by 2050 that is 6% of the GDP in 2050 only. Averagely, in the next 30 years India will lose about 3% of GDP. This figure sores even more when we reach to 2070, wherein India will lose about US$35 trillion i.e., 12.6% of the GDP.6
Yet, aspiring developmental goals without considering climate change is futile. At the same time, the huge and urgent developmental challenges cannot be ignored. Hence, both international efforts to alleviate the degree of climate change and domestic efforts to acclimatize the global warming already locked from earlier emissions.7
The literature review on impact of climate change on economic development is quite overwhelming. It is not only in depth but also has good coverage. Although, literature pertaining to developing countries is not in abundance. However, it has been suggested that climate change do leave an impact on the economy and a transition to low carbon economy is possible only if the measures benefit economically.8
Through this paper, we shall be highlighting how climate change is impacting the economy of India. Such nearly backward countries are not responsible for the large-scale emissions that are jeopardizing the present and future generations. While who is responsible or who is not for current climatic adversities, is very subjective. Herein, we shall be presenting why such immediate policy changes meet reluctance and how despite this India can reach its developmental goals in the long run.
Materials and Methods
This paper presents a qualitative research based on data extracted and analyzed from crucial government documents like “Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region Report 2020” and research papers.9 Initially, we have tried to express the climate change briefly supported via facts and figures. Appropriate figures for time series analysis of temperature and monsoon have been included for a comprehensive interpretation of the trends from available data. Further we have given context to the pillars that make up the Indian economy and how they have been suffering as a consequence of climate change. We have emphasized on agriculture, livestock, infrastructure, and low-income households. Then we have discussed the energy needs that are crucial to development and how they present a difficult situation. We have discussed how meeting energy needs in developing countries leads to climate changes. Further we have stressed on how we can aspire for growth and development, even while keeping a check on climate change with valuable suggestions.
Regional Indian Climate Change
The climate of India is quite diversified in nature, from the Himalayan crown to the flat beaches, a significant transition in climate is visible. The climate varies from the freezing temperatures of the Himalayan Mountains to the tropical climatic conditions of southern India. The eastern states received the maximum rainfall while the western states dried of water make up the arid deserts of Thar and Great Indian Desert.
Such a vastness of climatic conditions has always benefited India. However, in recent years many reports have projected the possibility of irreversible climatic changes. The IPCC 2021 report of climate change came as a shock for many as the report solidified its case of climatic worries and warned of severe consequences. For India too, in the past, many documents and reports have repeatedly shown the changing climatic trends and their impact on the Indian dimensions. The amplitude of the “CO2 mixing ratio” has been rising gradually for the last few years. How has the climate so far changed…?
Temperature
A report on the assessment of Indian climate (“Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region Report 2020”)9 has shown that the annual mean, minimum and maximum temperatures for the period of 1986-2015 have shown considerable warming by 0.15 °C, 0.13 °C, and 0.15 °C respectively. A significant change in pre-monsoon temperatures has also been seen with the highest warming trend. Heat extremes have increased over pan India during the period of 1951-2015. An ascending warming trend has been seen in the recent 30 years. An increase in the warmest day and warmest night temperatures along with the coldest night temperature has been observed since 1986. For India, an earlier IPCC report has forecasted the increased number of heat waves, and hot days. Deaths due to heat stress have also risen in recent years.10
The Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature has been increasing with an average increase of 1.0 °C which was higher than the global average (0.7 °C) during 1951-2015. It has been speculated that around 90% of heating/warming is due to emissions caused by human activity and this will continue in the upcoming future in case of both high and medium emissions.11
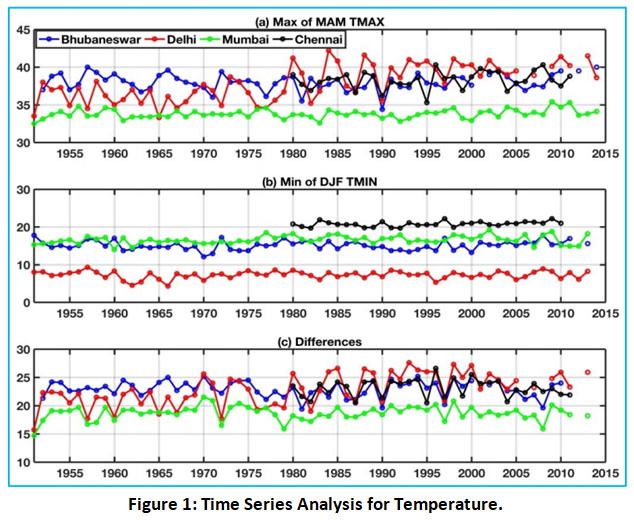 |
Figure 1: Time Series Analysis for Temperature. Click here to view Figure |
The first graph is for largest maximum temperature for the months of March to May. The second graph is for the lowest minimum temperature for the months of December to February. The third graph is the difference between the two temperatures denoted for four major climate zones that are Bhubaneswar (blue line), Mumbai (green line), and Delhi (red line) during 1951-2015 and Chennai (black line) during 1980-2015.
The calculations and graphical analysis have been done using Mann Kendall rank test with a 90% significance level. From the Figure 1, it can be observed that there is high variability in the minimum and maximum temperature in the later years (1981-2015).12 These observations are in compliance with the theoretical data that has been published in climate assessment reports (Table 1). Below mentioned is tabular data for temperature increase for different months/seasons during a year.13
Table 1: Temperature Trends for different Months/Seasons during the Years 1986 - 2015.
|
Season |
Temperature Trends for the Period 1986 – 2015 (0C/ Decade) |
||
|
Mean |
Minimum |
Maximum |
|
|
Annual |
0.15±0.09 |
0.13±0.10 |
0.15±0.10 |
|
Winter (December - February) |
0.05±0.16 |
0.07±0.18 |
0.03±0.20 |
|
Pre-Monsoon (March - May) |
0.26±0.17 |
0.20±0.16 |
0.29±0.20 |
|
Monsoon (June - September) |
0.11±0.12 |
0.11±0.08 |
0.10±0.17 |
|
Post- Monsoon (October - November) |
0.17±0.17 |
0.19±0.20 |
0.14±0.22 |
Rainfall
As the temperature increases, its effect can be easily seen on the rainfall of the region. This is because warm air holds greater moisture in comparison to cold air and warm water evaporates at a faster pace. A cumulative effect of these is seen in the rain. These are causing more frequent heavy downpours which are not usually common. During the period of 1950 to 2015, there has been a threefold increase in heavy precipitation in the central Indian region.14
While extreme precipitation has considerably risen over the subcontinent, however, an extremely contrasting observation has also been made. According to the assessment report, there has been an overall plummeting rainfall trend in the annual all-India and mean summer monsoon precipitation in the period of 1951 to 2015. This has been observed largely in the Western Ghats and Indo-Gangetic Plains. The cause for this trend is a notably increased concentration of anthropogenic (human-caused) aerosols over the northern hemisphere. Urbanization, improper land use, and increased anthropogenic aerosols are considered the main factor behind the increased localized rainfall and overall mean rainfall decrease.
The time scale analysis of rainfall for the current year during the monsoon season from June to September depicts intense monsoon variability with frequent maximum peaks (Figure 2). As expected from theoretical research, the monsoon is becoming severe.
India receives most of its rainfall from the monsoon. This exotic wind pattern has been responsible for a significant amount of rainfall over the Indian subcontinent. Hence, a major impact of climate change has been seen on this pattern. It has been projected that the monsoonal precipitation is going to become more severe in the future due to an increase in mixture content as a consequence of increased temperatures.
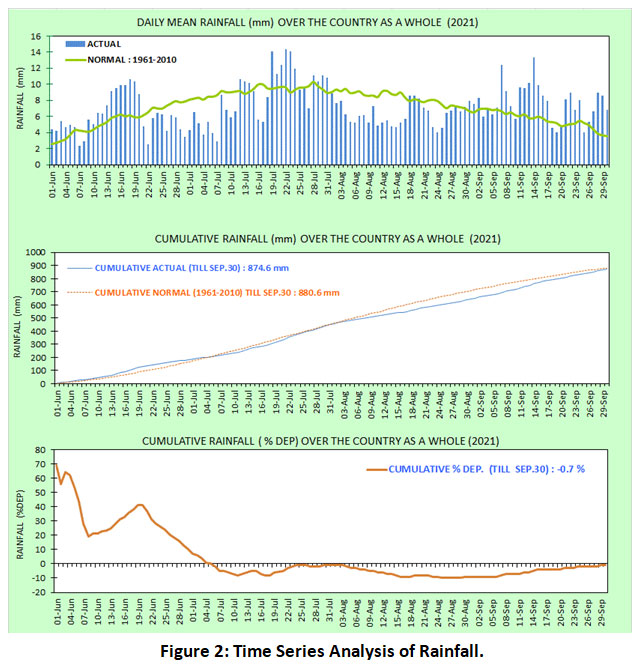 |
Figure 2: Time Series Analysis of Rainfall. Click here to view Figure |
The first graph is for the monsoon season from June to September. The second graph is a comparison of the cumulative rainfall for the monsoon season for the current year (2021) and from 1961-2010. The third graph is the depreciation in monsoon rainfall for the current year.15
Drought
During the period of 1951 to 2015, the number and geographical extent of droughts have risen over the subcontinent. Drought severity is mainly observed in parts of central India and parts of Indo-Gangetic Plains. These observations are in-line with a decrease in mean summer season monsoon precipitation. However, at the same time rise in the occurrence of localized rainfall has increased the probabilities of fatal floods. Climate models have projected a rise in the extent, occurrence, and severity of droughts over pan India while flood propensity is predicted to be higher in Himalayan River basins. Continuous drought in the years 1999 and 2000 led to a steep decrease in the groundwater tables of the northwest region and the 2000-2002 droughts caused extreme crop failure which led to the worst massive starvation and affected 11 million people in Orissa.16
Himalayan Region
According to the “Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region report 2020” of India,9 substantial warming in the Himalayan region has been observed in the twentieth century. The warming is quite prominent in the Hindu Kush Himalayan (HKH) regions that is having the most area with non-temporal ice cover after the south, and north poles. The annual mean temperature in the HKH region has been incessantly increasing by 0.1 °C per decade during 1901-2014, which further increased at about 0.2 °C per decade during 1951-2014. At elevated regions (>4000m), the warming is quite strong, as high as 0.5 °C per decade. It has been further projected that the HKH region will keep on warming in the range of 2.6-4.6 °C by the end of the 21st century.
Economy and Climate Change
Positively, the Indian democracy has resulted in equity moderately greater than the global average and the dependency ratio is also relatively greater. Nonetheless, the poor living standards of people involved in agriculture and people born into socially and economically backward castes and regions limit the robustness of the wholesome economy. It is possible and predicted that climate change will rip off the existing economic standards of these people so much so that it will result in severe taxes on the economic and industrial assets of the state and central government.
It has been projected that climate change can deplete India’s GDP by circa 2.6% by 2100 even while capping the global temperature rise below 2 °C. In a scenario where global temperature also keeps increasing (4 °C), this depletion is projected at 13.4%. These figures are an outcome of the changes in precipitation and temperature levels, and the impact of climate change on labor productivity. Labor productivity may as well get affected by endemic vector-borne diseases like malaria, dengue, etc. The probability of the outbreak of such diseases increases due to climate change.17
Nevertheless, gauging the exact financial and economic costs of climate change is a herculean task and also appears complicated due to uncertainties at every step. The absolute cost of flooding, heatwaves, cyclones, water scarcity, sea-level rise, and other climate-related hazards can be determined by the level and direction of economic development, the solutions opted in infrastructure development, spatial planning in the future, and the intermingling of hazards and how they will multiply each other. On top of everything, global warming will have a major role to play in determining the economic costs.
Agriculture
Even after 74 years of independence, India is still mostly an agrarian economy. About 50% of the Indian population is still directly or indirectly dependent on agriculture for meeting essential needs. If the harvest is good enough, the economy also benefits. So, Indian economic development can be seen on a proportional line with agriculture. However, agriculture is itself dependent on natural forces like the monsoon, rainfall and temperature.
Agriculture contributes about 50% to the Indian economy. Although this has been decreasing recently, yet even today, slight upheavals in agriculture directly impact the economy. When we discuss the impact of climate change, its impact on agriculture can’t be ignored. Even in its raw and backward form, agriculture has been supporting the backbone of the Indian Economy. In many parts of the country, farmers are dependent on the monsoon for irrigation and good harvest. There is a huge demand for another green revolution as the benefits of the first green revolution was limited to only a few parts of the country, mainly Punjab and Haryana. Admittedly, the effects of climate change will be felt chiefly on the agricultural sector and the corresponding water requirements and availability.
Agriculture production in the North region depends on spring snowmelt to replenish water supplies. It has been predicted that earlier snowmelt on account of climate change can substantially reduce the water table during the growing season impacting production. The southwest monsoon is critical for agriculture as it provides for about 80% of rainfall to the country. This also acts as an important tool to determine optimal dates for plantings. Many models have projected that India will suffer from intense and longer summer monsoon and weak and short winter monsoon. At the same time, pronounced warming will contract overall rainfall.18 Monsoon-dependent agriculture will see profound transitions. Without proper or no irrigation, landless agriculture laborers, and small farmers will face loss of livelihood and extreme food shortages. Most of these will go to cities in search of work and economic prospects.19
Numerous people will be affected by decreased food productivity leading to malnutrition, hunger, diseases, etc. This will also increase the burden of providing assistance to these small landholders on the state and center. There will be increased demand for infrastructure following a major internal migration will occur, owing to decreased agriculture output and income, to urban areas. The need to replace the existing infrastructure (e.g., in the transportation and energy sectors, irrigation systems) due to climate change will cause greater economic costs.
Livestock
India has the most livestock population globally. This is primarily because of the large-scale milk production, nutrient recycling (manure), household capital, draft animals, etc. These animals are used as household capital in landless households. Many low-income rural families even use animals as means of transportation and consider livestock as a potential economic asset. However, the reproduction and production of livestock are affected by increasing temperatures. Heat stressors reduce feed and fodder intake and increase vulnerability to diseases. Feeding is affected as fodder gets expensive due to increasing agricultural - produce costs. One example of a heat stressor was the outbreak of foot and mouth disease in cattle. 52% (Andhra Pradesh) and 84% (Maharashtra) were found to be affected, owing to high temperature, rainfall, and humidity conditions. A disease called mastitis occurs in dairy animals during hot and humid weather.20
Infrastructure
A good and sound infrastructure contributes a great deal to the economy of a nation. Without proper infrastructure many economic prospects and projects are desolate. However, the increased extremes of natural calamity as an outcome of climate change have deeply affected the infrastructure.
Palpably, in India, 14% of the annual maintenance and repair budget is spent on maintaining the Konkan Railway. Consequently, tracks, cuttings, and bridges are damaged each year due to uneventful weather conditions. Landslides remain a constant source of worry. During heavy rains, the developmental projects have to be stalled for more than seven days leading to extended costs. Massive destruction of on-site material also takes place.21
In the last few decades, as flood-like situations have prominently risen, a major portion of the budget goes to disaster relief. India spent $3 billion of economic damage caused by floods in the last decade which is 10% of the global economic loss.22 In 2020, cyclone Amphan distressed around 13 million people and caused more than $13 billion in damage in the region.23 In such a disaster, the direct impact can be seen on low-income households which are displaced and find it difficult to accumulate assets to enhance their security.
Low Salaried/Income Household
Low-income households are more susceptible to economic losses due to climate change. This is because they settle in densely populated regions that lack basic infrastructure and services like paved roads, safe and piped water, decent housings, drainage, etc. it has also been found that many people live in low-lying coastal areas, steep slopes, and flood-prone regions as the cost of land is cheaper.24
Furthermore, these people will also be directly affected by a combination of increased cereal prices, a slower economic growth rate due to climate change, and declining wages in the agricultural sector. It is feared that if the situation persists, it might increase the national poverty rate by 3.5% in 2040 contrastingly greater than what is expected in a zero-emission-warming scenario.25,26
Energy Economy and Climate Change
Energy is required to sustain not only people but everyone all around. It lights homes, runs factories and vehicles, draws water, and much more. In a way, energy needs and production are also a measure of economic progress. Hence, it won’t be wrong to conclude that energy dynamics and climate change are inseparable. Climate change has a direct consequence on the energy demands and production of a country and vice-versa. The extremism of climate change is becoming a major cause of concern for the energy sector of developing and under-developed countries. Owing to a stressed economy, lack of technological innovation, and infrastructure to sustain new technologies, these countries are forced to stick to the conventional sources of energy. These sources of energy largely depend on fossil fuel burning and hence contribute significantly to Green House Gas (GHG) emissions.
The per capita demand for energy is about 1/10th of the OECD average with a constantly increasing demand - 3.2 percent per year (2000-2005). It is speculated that the energy needs of India will double by 2030 (considering the growth rate of 6.3% GDP annually).27 In India major energy usage is for producing electricity and transportation fuels. Most of these energy needs are met by domestic coal and petroleum reserves along with imported oil. Fossil fuels contribute about 82.7%, hydropower 14.5%, and nuclear only 3.4%. The transportation sector is supported by imported fuels as the domestic production is extremely less, about 785,000 bbl/day opposed to a demand of 2.45 million bbl/day. The IEA has described this situation as a system fueled “largely by coal and combined renewables and waste, with much smaller but growing shares of gas, oil, hydro, and nuclear".28
At the same time, the growing inequality in energy demand and supply cannot be ignored. As development paces, the demand for energy increases. However, the current production is not sufficient. Circa 401 million people live without electricity, use of fuel wood and dung is prevalent leading to greater than 400,000 premature deaths yearly, mostly of children and women. Energy poverty can be seen in India as the economy booms and the economic conditions have benefited the “haves” but not the “have-nots”.26 Income inequalities are largely responsible for this economic disparity. Evidently, electrical vehicles are being made available for Indians, however, their soaring prices make them unappeasable for the majority of the population.
To bridge this gap, India must heavily invest in providing energy to all its people. However, this can’t happen without involving fossil fuels in the picture in the short run. In such a scenario, for India the battle becomes more difficult as it can’t severe itself from the conventional means of energy generation and employment. The discontinuation of coal will affect employment of numerous and at the same time putting millions of people into darkness and shut hundreds of productions units. This will again add to the woes of economy.
Results and Discussions
By now we have seen the existing climatic variations and the challenges presented to the pillars of economy. We now have an idea as to how climate change has affected us in every possible way. Perhaps something unavoidable. Yet, development measures themselves possess great risk when it comes to climate change.
Rainfall
As evident from the above discussion, the temperatures are rising consequently of climate change. This will result in escalated evaporation of water and accumulate abundant water for precipitation, thereby leading to flood-like situations. Similarly, increase in the evaporation rate of water and tremendous change in wind pattern will lead to decreased rainfall leading to drought like situations. Hence, there will be an overall increase in storms and strong rainfall. So, areas in their direct contact will experience excessive precipitation. While areas away from them will experience water scarcity.
Temperature
Temperature is itself regulated by the water cycle and the atmospheric gasses. With an increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases, the temperature of earth will rise as more and more heat will get trapped in the atmosphere. All this is powered via climate change.
Agriculture
Both temperature and rainfall directly impact the agriculture. The reason being certain crops need certain physical condition for proper growth. Hence, climate change can make the growth of a particular crop difficult. For example, crops that need lower temperature will suffer from lower yields due to global warming (heating of the earth atmosphere). At the same time, crops needing less amount of water will get destroyed due to increased precipitation.
Impact of Development on Climate Change
The impact of development on climate change is very subjective and highly improbable. The reason being, the impact of development varies according to the different techniques used. However, as a summation it can be concluded that conventional mode of development like dependence on fossil fuels have degraded the climate and contributed to maximum climate change. As the time changed, and policies started adopting greener methods of development, there have been positive impact on the climate change. But the impact of development before the 20th century had impacted the climate in the most non-ignorable ways. It may be noted that the countries contributing to global pollution levels, global warming, and climate change are developed economies which experienced development through the 19th and 20th century. While countries who are either developing or underdeveloped contribute less to climate change parameters.
Economy and Environment Go Hand In Hand
India is blessed with enormous alternatives to meet its developmental needs. Stronger carbon emission targets can be met without compromising on developmental aspirations. The gradual decrease in public support for coal and improvement in electricity distribution can help to free fiscal space when public debt is increasing. This can also help in the generation of economic diversifications in the regions heavily dependent on coal for revenues and employment.
Promoting clean and green electricity generation can help in diverting the burden from fossil fuels and reducing air pollution while generating more employment opportunities. Developing new mass transit systems and extending the present ones can reduce vehicular emissions while blooming employment. It will also stimulate economic growth through agglomeration economies in the future. Conservation and enhancement of wetlands and forests will support agricultural productivity, sequester CO2 emissions, and enhance resilience power to environmental shocks.
New metro systems are being developed and ambitious plans for vehicles and full electrification of railways are imperative. India has also started considering climate change in its policies for agriculture and water. Many times, the low-carbon options are more affordable than their counterparts and they also help in addressing socio-political needs urgently like the cleansing of air and access to quality jobs and services. The low-carbon alternatives will help in raising the standards of living and reduce GHG emissions simultaneously.29,30,31,32
The Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) report of India aims at 40% of energy generation from clean energy and a 33–35% reduction in emission intensity of GDP by 2030. India today is spending on energy-efficient lighting and renewable electricity more than ever.33,34
India has committed to reduce its carbon emission by 1 billion by 2030 and reduce the dependence of the economy on carbon by 45% by the end of the decade at the COP26 Glasgow summit. It also aspires a net-zero carbon emission by 2070.35
The below mentioned can be considered as a pivot point while forming climate policies.
- Solar Energy
India has been recently investing a lot in solar energy. This will help to eventually shift from fossil-fuel-based electricity generation. At the same time, it will create more employment opportunities in the short and long term. It can also help in reducing the gender gap in the economy. The people already involved in fossil fuel-based jobs can be trained for this switch, thereby protecting their employment prospects. The development of solar villages will not only help in raising the standards of all people but also cap GHG emissions.
- Waste Management
Mismanagement of waste is also leading to widespread water pollution and disturbs the ecological balance. In many areas, people are exposed to untreated waste leading to poor health and reduced life expectancy. Currently, India does not have any clear policy mandate on waste management. In recent years a lot of efforts have been given to solid waste management, but they remain lacking. The development of waste-selective management plants like waste gasification will tackle this problem. Building the infrastructure of these plants and future maintenance will open new employment opportunities for both skilled and unskilled laborers.
- Gasification
Gasification is also another field of interest when it comes to reducing climate change. At present many alternatives for petrol and diesel are present. Organic fuels like methanol and biofuels can essentially help motivate people to go green without any compromise on quality. In many countries, gasification is already used as an alternative to fossil fuels in countries like Japan. India should also join them. It will help in achieving the short-term goals of climate change.36
- Electrical Vehicles
Electrical vehicles are the future of this world. In many countries, a lot of stress is already being given to EVs. However, these come at greater costs and are not affordable without compromise on quality. So, they should be developed as long-term goals. Special highways and express easy should be built to initiate the process.
- Afforestation
Forests are known for regulation rainfall and temperature. Restoration of the lost forest cover is essential. This will help in meeting needs and maintaining the ecological balance. A great amount of CO? will also get absorbed leading to maintained CO? levels. At the same time, precipitation and temperature will also be checked. This will improve/ maintain agricultural productivity.
- Alternatives for Pollution-Causing Substances
India should invest a great deal into its Research and development sector. Explorations and innovations for alternatives to existing pollution-causing substances will help in meeting the desired targets as soon as possible.
Conclusion
We have seen how climate change is affecting the pillars of Indian Economy (Agriculture, livestock, etc.) and why adopting harsh climate policies often meet reluctance (energy economy). Although India is the only G20 nation with a 2 °C compatible emissions, there is no harm for it to adopt an even more stringent approach in reducing climate change. The adoption of more carbon-efficient and resilient policies like National Clean Energy Fund and International Solar Alliance will enable it to climate-proof its future developmental endeavors. This will require the collective efforts of the government and the people. This is possible when people abide by the rules and regulations formed by the government towards reduction of climate change. At the same time, the government also boosts the motivation of the people via rewards. Recently, the Indian government at the COP26 summit committed to a net zero carbon economy in the near future. The words ‘climate’ and ‘economic-development’ are therefore inevitably and closely linked in India for decades to come.
Funding Source
No funds, grants or other support was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Acknowledgement
We gratefully acknowledge Ramjas College, University of Delhi and Central University of Jammu for providing the financial support and assistance to the authors.
References
- Zaveri, E., Grogan, D.S., Fisher-Vanden, K. Frolking, S., Lammere, R.B., Wrenn, D.H., Prusevich, A., Nicholas, R.E. Invisible water, visible impact: groundwater use and Indian agriculture under climate change. Environmental Research Letters, 2016; 11(8) 084005: 1-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/8/084005.
CrossRef - Mekonnen, M.M. and Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Science Advances, 2016; 2(2): e1500323. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1500323.
CrossRef - National Intelligence Council Special Report NIC 2009-03D. India: Impact of climate change to 2030 a commissioned research report, 2009. https://www.dni.gov/files/documents/climate2030_india.pdf.
- Fogel, R.W. Capitalism & democracy in 2040: Forecast and speculations. NBER Working Paper 2007; 13184: 1-23. http://www.nber.org/papers/w13184.
CrossRef - Global Change Data Lab. Our world in data: cumulative CO2 emissions by world region. Online dataset, 2021. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/cumulative-co2-emissions-region.
- Phillip, P., Symons, W., Ibrahim, C., Hodges, C., McGrath, M. India’s Turning Point: How climate action can drive our economic future, 2021, 1-46. https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/in/Documents/about-deloitte/in-india-turning-point-noexp.pdf.
- Dubash, N.K. An introduction to India’s evolving climate change debate: from diplomatic insulation to policy integration. India in a warming world: integrating climate change and development, Oxford Scholarship online, 2019. DOI: 10.1093/oso/9780199498734.001.0001.
CrossRef - Batten, S., Sowerbutts, R., Tanaka, M. “Let’s Talk About the Weather: The Impact of Climate Change on Central Banks”, Staff Working Paper No. 603, Bank of England, 2016; 1-38.
CrossRef - Krishnan, R., Sanjay, J., Gnanaseelan, C., Mujumdar, M., Kulkarni, A., Chakraborty, S. Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region: A Report of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Government of India, 2020; ISBN: 978-981-15-4329-6, 1-243. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007%2F978-981-15-4327-2.
- Cruz, R.V., Harasawa, H., Lal, M., Wu, S., Anokhin, Y., Punsalmaa, B., Honda, Y., Jafari, M., Li, C., Huu Ninh, N. Asia. Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, P.J., Hanson, C.E. Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2007; 469-506.
- Deser, C., Phillips, A.S., Alexander, M.A. Twentieth century tropical sea surface temperature trends revisited. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010; 37: L10701. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL043321.
CrossRef - Saikat, P., Sourav, S., Samiran, M. Time series analysis of observed maximum and minimum air temperature at four urban cities of India during 1951-2015. Mausam, 2021; 71 (1): 57-68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.54302/mausam.v71i1.6.
CrossRef - Sanjay, J., Revadekar, J.V., Ramarao, M.V.S, Borgaonkar, H., Sengupta, S., Kothawale, D.R., Patel, J., Mahesh, R., Ingle, S., Achuta Rao, K., Srivastava, A.K., Ratnam, J.V. Temperature Changes in India. Assessment of climate change over the Indian region, Springer, Singapore, 2020; pp 21-45. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4327-2_2.
CrossRef - Roxy, M.K., Ghosh, S., Pathak, A., Athulya, R., Mujumdar, M., Murtugudde, R., Terray, P., Rajeevan, M. A threefold rise in widespread extreme rain events over central India. Nature Communications, 2017; 8(708): 1-11. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00744-9.
CrossRef - All India Rainfall Time Series, India Meteorological department, Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, 2021. https://mausam.imd.gov.in/imd_latest/contents/rainfall_time_series.php.
- Mallya, G., Mishra, V., Niyogi, D., Tripathi, S., Govindaraju, R.S. Trends and variability of droughts over the Indian monsoon region. Weather Clim. Extremes 2016; 12: 43-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace. 2016.01.002.
CrossRef - Kahn, M.E., Mohaddes, K., Ryan, N.C., Ng, R.N., Pesaran, H., Raissi, M., Yang, J. Long-term macroeconomic effects of climate change: a cross-country analysis. IMF Working Paper, WP/19/215, 2019. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2019/10/11/Long-Term-Macroeconomic-Effects-of-Climate-Change-A-Cross-Country-Analysis-48691.
CrossRef - Ruosteenoja, K., Carter, T.R., Jylhä, K., Tuomenvirta, H. Future climate in world regions: an intercomparison of model-based projections for the new IPCC emissions scenarios. The Finnish Environment 644, Finnish Environment Institute, 2003; 83pp. https://www.ipcc-data.org/documents/scatter_plot_report.pdf.
- McLean, R.F., Sinha, S.K., Mirza, M.Q., Lal, M. Tropical Asia, in The Regional Impacts of Climate Change: An Assessment of Vulnerability. eds. Watson, R.T., Zinyowera, M.C., Moss, R.H. A Special Report of IPCC Working Group II, Published for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press. 530pp. 1998). https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2020/11/The-Regional-Impact.pdf.
- Whitman, S. World Poverty; 2006. http://www.fao.org/newsroom/en/news/2006/1000392/index.html.
- Wilbanks, T.J., Lankao, P.R., Bao, M., Berkhout, F., Cairncross, S., Ceron, J.-P., Kapshe, M., Muir-Wood, R., Zapata-Marti, R. Industry, settlement and society. Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, P.J. Hanson, C.E. Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2007; 357-390. https://www.alnap.org/help-library/industry-settlement-and-society.
- Hallegatte, S., Rozenberg, J. Climate change through a poverty lens. Nature Climate Change, 2017; 7: 250–256. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3253.
CrossRef - Nagchoudhary, S., Paul, R. Cyclone Amphan loss estimated at $13 billion in India, may rise in Bangladesh. Reuters, 23 May 2020. www.reuters.com/article/us-asia-stormindia/cyclone-amphan-loss-estimated-at-13-billion-in-india-may-rise-in-bangladeshidUSKBN22Z0HE.
- Satterthwaite, D., Archer, D., Colenbrander, S., Dodman,D., Hardoy, J., Mitlin, D., Patel, S. Building Resilience to Climate Change in Informal Settlements. One Earth. 2020; 2 (2): 143-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2020.02.002.
CrossRef - Jacoby, H., Rabassa, M., Skoufias, E. Distributional implications of climate change in India. Policy Research Working Paper 5623, 2011. Washington DC: World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/1813-9450-5623.
CrossRef - Skoufias, E., Rabassa, M., Olivieri, S. The poverty impacts of climate change: a review of the evidence. Policy Research Working Paper 5622. Washington DC: World Bank, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1596/1813-9450-5622.
CrossRef - IEA - International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook: China and India Insights, IEA, Paris, 2007. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2007.
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, International Energy Agency, Statistics on the web, 2006. https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics.
- IEA – International Energy Agency. India energy outlook 2021. International Energy Agency, 2021. India Energy Outlook 2021 – Analysis - IEA.
- Dubash, N.K. The politics of climate change in India: narratives of equity and cobenefits. WIREs Climate Change, 2013; 4: 191–201. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.210.
CrossRef - Colenbrander, S., Gouldson, A., Roy, J., Kerr, N., Sarkar, S., Hall, S., Sudmant, A., Ghatak, A., Chakravarty, D., Ganguly, D., Mcanulla, F. Can low-carbon urban development be pro-poor? The case of Kolkata, India. Environment and Urbanization. 2016; 29(1): 139–157. https://doi.org/10.1177%2F0956247816677775.
CrossRef - Tibrewal, K., Venkataraman, C. Climate co-benefits of air quality and clean energy policy in India. Nature Sustainability. 2020; 4: 305-313. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-020-00666-3.
CrossRef - Naswa, P., Garg, A. Managing climate-induced risks on Indian infrastructure assets. Current Science, 2011; 101(3): 395 - 404. https://www.jstor.org/stable/24078518.
- Sadhukhan, B. FEATURE: Indian infrastructure must be climate-proofed to the core’. Cape Town: Climate & Development Knowledge Network, 2019. https://cdkn.org/2019/01/indianinfrastructure-must-be-climate-proofed-to-the-core/?loclang=en_gb.
- https://www.livemint.com/industry/energy/indias-cop26-commitments-to-help-with-new-green-technologies-icra-11641385538944.html.
- Ciuta, S., Tsiamis, D., Castaldi, M.J. Chapter Four - Field Scale Developments, Gasification of Waste Materials, Academic Press, 2018; Pages 65-91, ISBN: 9780128127162. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812716-2.00004-2.
CrossRef






