Study of the Effect of Air Pollution on Wheat
Rajesh Kumar Singh1
1
Department of Chemistry,
Jagdam College,
J P University,
Chapra
India
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.6.2.15
Wheat is a very important crop of Indian farmers. Most of the people fooding depend upon wheat. There are several eatable food products prepared by wheat. Wheat is cultivated mostly in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal. Recently in these states industrialization and infrastructure development work are going very fast causing huge amounts of pollutants and particulate entering into the atmosphere. Pollutants are oxide of carbon, oxide of nitrogen, oxide of sulphur, oxide of chlorine, chloride ions, ammonia, organic acids and aldehydes where as particulates are dust, smoke, mist and fog. Particulates are deposited on the surface of wheat. Some of these particulates are hydroscopic in nature. They absorb pollutants and form acids. These acids in turn develop micro electrochemical cell with flower of wheat which destroy flowering of wheat. Other factors are acid rain, global warming and depletion of ozone layer also affect the production of wheat.
Copy the following to cite this article:
Singh RK. Study of the Effect of Air Pollution on Wheat. Curr World Environ 2011:6;291-293 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.6.2.15
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Singh RK. Study of the Effect of Air Pollution on Wheat. Curr World Environ [serial online] 2011;6:291-293. Available from: http://www.cwejournal.org/?p=1434
Download article (pdf) Citation Manager Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 2011-10-10 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 2011-12-17 |
Introduction
Wheat is cultivated in the basin of Ganga river, Yamuna, Gomati and other areas. These areas are flooded with industries1-5 like chemical, coal, fertilizer, petroleum refinery, food processing, transport industry, coal power, hydropower, drug industry, pulp and paper industry, paint and dyes, sugar industry, wine industry, water bottling plant, juice factory, milk processing. These industries release huge amount of pollutants6-9 like inorganic, organic and particulates material. They pollute air and that polluted air produces several problems for living and nonliving things. Inorganic pollutants are oxide of carbon (CO, CO2), oxide of nitrogen (NO, N2O, NO2), oxide of sulphur (SO2, SO3), oxide of chlorine, chlorine ion, ammonia and oxide of metal. Organic pollutants are organic acid, aldeyhde, ketone, amine etc. Particulates10-11 are dust, smoke, mist, pollen, bacteria and fog.
Wheat flowering period starts from December to February. Particulates are scattered into the atmosphere which are deposited on the surface of wheat. Some of these particulates are hydroscopic12 in nature. They absorb moisture13 from the atmosphere. The moist particulates14 absorb oxide of carbon, oxide of nitrogen, oxide of sulpher, oxide of chlorine and chlorine ion to form carbonic acid, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, hypochlorous acid and hydrochloric acid. These acids are highly corrosive in nature. They create hostile environment for wheat flowers. The corrosive acid produces micro electrochemical cell with wheat flower thus electrochemical reaction occurs on the surface of wheat flowers in this way flower of wheat get destroyed and conversion of flowers into wheat is decreased.
Methodology
For this work certain wheat growing areas were selected like Ludhiyana in Panjab, Hishar in Haryana, Lucknow in Uttar Pradesh and Patna in Bihar. The study of the characteristic behaviors of inorganic, organic and particulates pollutants and their effect on wheat flowers were done in detail. Monitoring works started during period of December to February. Corrosive gases and their acidic character were determined with the help of Pen types PH meter.
Result and Discussion
Wheat is main food of human being. Our country is highly populated. Our public have so many basic needs like food, clothe, house, education, hospital, electricity, transport, road, industry and telecommunication. For the completion of these basic needs we do not utilize our natural resources in proper manner. Man creates its own environments. Recently infrastructure development works are going very fast in several sectors like industry, agriculture, power generation, construction etc. These sectors have major role in pollution of environment.
The main features of wheat depend upon temperature, humidity and nature of surrounding environment during its flowering period. The concentration of corrosive gases, particulate materials and humidity are high so they form H2CO3, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO and HCl. These acids produce H+ ion that ion starts electrochemical reaction with wheat flowers. Due to this reaction flowers connectivity become weaker and finally they are detached with main branch of wheat plant. During the formation of acids exothermic reaction occurs and heat is evolved which increases the temperature of surrounding of wheat flowers, thus flowers are easily separated from its main branch.
The chemical reactions among them are written as:
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
NO + O2 → NO2
NO2 + H2O → HNO3
SO2 + O2 → SO3
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Cl− + H2O → HCl + ClO−
The above mentioned acids are dissociated and released H+ ion that ions in the presence of electrolytes develop an electrochemical cell causing oxidation and reduction reactions to start on the surface of wheat flowers. The electrochemical reaction is expressed as:
Half Oxidation Reaction
CH2O → CO2 + 2H+ + 2e
Half Reduction Reaction
2H+ + 2e → H2
This chemical reaction indicates that corrosive pollutants are corroding the wheat flowers. The PH values of above mentioned cities are recorded in Table 1 and bar graph plots between the PH values of corrosive pollutants and its concentrations in different cities. The results of Table 1 and Fig. 1 show that the concentration of H+ ion in Ludhiyana city is higher than that of Hisar. Likewise the concentration of H+ ion in Lucknow is greater than Patna and wheat crops of these areas are badly affected by pollutants.
 |
Table 1: PH values of corrosive pollutants in different Cities Click here to View table |
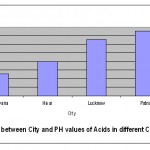 |
Figure 1: Plot between city and pH values of Acids in different cities Click here to View figure |
The concentration of carbon dioxide and methane gases increases in atmosphere due to deforestation, industrialization and human waste decomposition. These gases produce global warming effect thus temperature of atmosphere is increased which exhibits bad affect on the wheat flowers. In lower level of atmosphere ozone is formed that ozone also disturbs wheat flowers.
O2 + UV → 2O
O2 + O → O3
Conclusion
Pollutants are very harmful for wheat flowers. They decrease its production. If its evolvement is not controlled at proper times, our country will become major loser of wheat. It is moral responsibility of the industrialists, scientists, intellectuals, social workers to provide good technology and public awareness against pollution.
References
1. “Air pollution” by A.C Stern, Academic press, New York, 1976.
2. B.J Pitts, Atmosphere Chemistry, Academic Press, Wiley, N.Y. 1986.
3. R.P Wayne, the Chemistry of the Atmosphere, Oxford Univ. Press, N.Y. 1991.
4. Murray J. McEwan and Leon F. Philips, Chemistry of Atmosphere, Halsted (Wiley), New York 1975.
5. “Air Pollution Control Theory” By M. Crwford, McGrow Hill, New York, 1976.
6. “Air Pollution” by H.C. Perkins, McGraw Hill, New York, 1974.
7. “Fundamentals of Air Pollution” by J. Williamson, Addison – Wesley, Reading, Masss. 1973.
8. “Pathways of Pollutants in the Atmosphere” by T.M.Sugden (Ed), The Royal Society, London, 1978.
9. “Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science” by G.M.Masters, Prentice Hall, New Delhi, 1994.
10. “Environmental Chemistry” by Nigel J. Bunce, Wuerz Publishing Ltd. Canada, 1991.
11. “Handbook of Pollution Control and waste Minimization” edited by Abbas Ghassemi, Marcel Dekker, Inc; 2002.
12. “Green Engineering – Environmentally Conscious Design of Chemical Processes by David T. Allen and David R. Shonnart, Prentice Hall, 2003.
13. “Enviroment – Problems and Solutions” by D.K.Asthana and Meera Asthana, S.Chand & Co. Ltd; New Delhi, 1998.
14. “Environmental Chemistry” by SE Manahan, Willard Grant Press, Boston, 1983.







