Flouorides in some ground water samples of Ambad Tehsil
K.N. Solunke1 , M.P. Gutte1 and S.R. Mirgane1 *
1
Department of Chemistry,
Jalna Education Society’s,
R.G. Bagdia Arts, S.B. Lakhotia Commerce and R. Bezonji Science College,
Jalna,
431 203
Maharashtra
India
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.3.2.27
Determination of fluoride concentration of thirty ground water samples and surface water samples from sites in Ambad Tehsil of Jalna district was carried out using ion selective electrode and out come of the results were discussed in the light of pollution status of the study area.
Copy the following to cite this article:
Solunke K.N, Gutte M.P, Mirgane S.R. Flourides in some ground water samples of Ambad Tehsil. Curr World Environ 2008;3(2):341-342 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.3.2.27
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Solunke K.N, Gutte M.P, Mirgane S.R. Flourides in some ground water samples of Ambad Tehsil. Curr World Environ 2008;3(2):341-342. Available from:http://www.cwejournal.org?p=150/
Download article (pdf) Citation Manager Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 2008-05-12 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 2008-08-17 |
Introduction
Ambad is considered to be oldest and religious town in Jalna district of Marathwada region. A famous temple of “Godess Matsyodari” is situated in Ambad town. A famous Temple of Lord ‘Jambuvant’ is situated near Jamkhed, 14 km away from Ambad town.
The residents of Ambad Tehsil usually use water from dug well and bore well for drinking and domestic purposes. There is a huge variation in the concentration of different species due to factors like depth, different land, under ground water conditions, rain conditions etc. The present work attempts to evaluate the ground water quality in Ambad Tehsil of Jalna district for potability.
Material Used
In the present study thirty ground water natural (borewell) samples were collected from different sites of Ambad Tehsil in brown glass bottles with necessary precautions and preserved as per the recommended procedures.¹
All the chemicals used were of AR grade, glass ware used were of ‘A’ grade. Double distilled (DD) water was used through out the work to prepare standard solutions.²
Method
Fluoride concentration in aqueous samples were determined with fluoride - Ion - Electrode (IRON) and ORION 407 A Ion Meter.
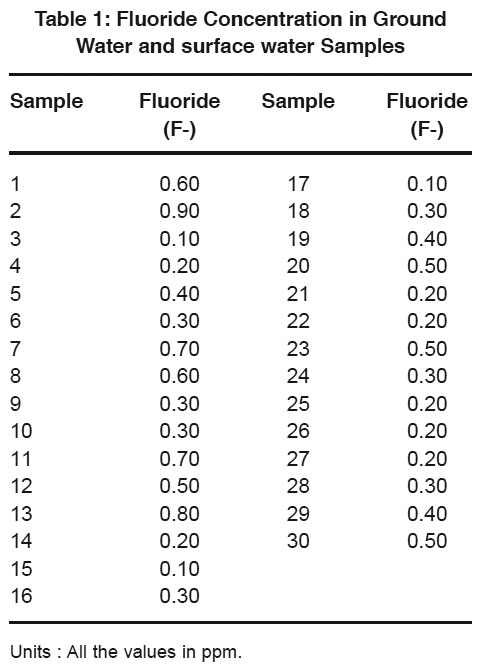 |
Table 1: Fluoride Concentration in Ground Water and surface water Samples Click here to view table |
A 25 ml of Aliquot was taken in polythene beaker and 25 ml of TISAB-III (Total ionic strength adujster bffer, ORION Application solution) was added. Ion Meter was standardised against solution of known fluoride concentration in the standard samples and read directly on the meter scale. The scale was calibrated in ppm of fluoride concentration in water.
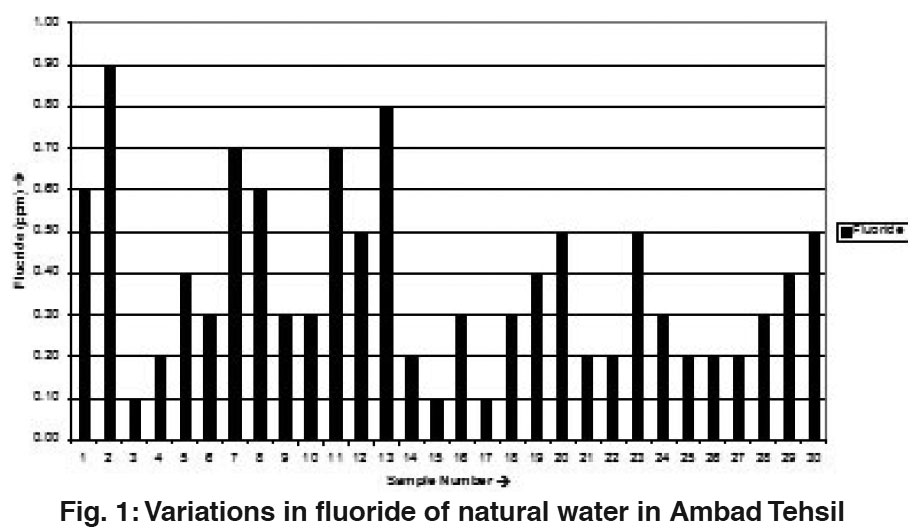 |
Figure 1: Variations in fluoride of natural water in Ambad Tehsil Click here to view figure |
Results and Discussion
Fluoride has little significance in industrial waters, but in amounts of 1 to 1.5 ppm it is an effective preventive of dental curies. Above this amount, fluoride may cause dental fluorosis and skeltol fluorosis. Such water should be defluoridated to reduce the fluoride concentration to the acceptable leveles.
In the present work fluoride concentration varied from 0.10 to 0.90 ppm. The values obtained are well below permissible limit, 1 ppm, prescribed by ICMR.3
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Principal Dr. R. S. Agrawal, Dr. S. M. Deshpande, Head of department, Jalna Education Society’s R. G. Bagdia Arts, S. B. Lakhotia Commerce and R. Bezonji Science, College, Jalna for providing necessary facilities and help for the present work.
References
- American Society for Testing and Materials, Annual Book of-ASTM Standard, Part-23, ASTM-Phifadelphia, (1972)
- A.l. Vogel, Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis 2nd edn., Longman & Green Co., London, (1985) 191.
- ICMR Manual of Standards of Quality for Drinking Water Supplies’, Spl. Rep. S.No. 44, ICMR, New Delhi (India), (1975).







