An Analytical Approach to the Issue of Passive Defense in Relation with Preservation of Urban Elements
Baghdadi Arash1 * and Eghtedarbakhtiyari Shahla2
1
Department of Urban Planning,
ShahreQods Branch,
Islamic Azad University,
Tehran,
Iran
2
Department of urban planning,
ShahreQods science and research branch,
Islamic Azad University,
Tehran,
Iran
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.9.2.15
Preserving territorial integrity and preventing from the attacks of enemies is the only common goal of all states and people of the countries on the earth. Passive defense which is mentioned abundantly today is one of the most important options in preserving this integrity. Passive defense is one of the special topics not only in Iran but also in many countries of the world because all efforts of a state are targeted at securing consent and welfare for its nation and preserving the national resources to produce income. Such incomes play substantial roles in creating substructures and superstructures. That is why preserving security and preventing from internal and international hazards is one of the basic programs of governments. Also spatial distribution of elements, combination of elements and main functions of the city which constitute to the structure of city are effective in the degree of vulnerability of a city against various dangers particularly military attacks. On this basis, the form and shape of the city entails a special attitude from passive defense perspective. Therefore, in the present research it has been attempted to introduce passive defense, define its theoretical fundamentals and application of this defense system in preserving and protecting the countries, and particularly their important and vital elements, express strategies for internalize passive defense in urban planning. Using this method may help save the cities against the crisis in critical situations through a coordinated and organized management process. Research method in this article is a combination of descriptive- explanatory and comparative methods; descriptive method has been used based on the information available in library deeds and documents.
Copy the following to cite this article:
Arash B, Shahla E. An Analytical Approach to the Issue of Passive Defense in Relation with Preservation of Urban Elements. Curr World Environ 2014;9 (2) DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.9.2.15
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Arash B, Shahla E. An Analytical Approach to the Issue of Passive Defense in Relation with Preservation of Urban Elements. Curr World Environ 2014;9(2). Available from: http://www.cwejournal.org/?p=6509
Download article (pdf)
Citation Manager
Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 2014-02-05 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 2014-05-25 |
Introduction
The subject of the passive defense has the age of human being. Early humans sheltered in caves, above the trees, and other natural shelters to protect themselves from wild animals attack and other enemies and also to allay concerns. With the form of early civilization in the world that are associated with invasiveness, human, distributed the basics of passive defense by armor and shields to individual protect and strong and high castles, towers to provide security for the people.
Presence of moat around the cities and establishing strong gateways to prevent sudden enemy attacks were common in all parts of the world. Passive defense measures against the threat of invasion were establishing fort built in the form of towers, gateways, castles, bastions, ramparts and fortified defensive positions. But after the invention of gunpowder and using it, passive defense subject also gradually changed.
During World War II using aircrafts, bombing of cities, industrial and investment centers and after that using rockets by Germans were started. Damages produced by these attacks to human and non military places were more frequent in comparison to First World War, and this led to give more concerns to passive defense by various countries.
Military powers of each country as a part of a national power are used in order to be ready to repel aggression operations and the ability to apply structural and functional forces. Whenever any of the elements of national power got weakness, military forces will encounter by strong structural and functional crises and should use strong management to solve the crises.
Crisis managers must seek ways to reduce the dimensions of the crisis. In many cases of crisis management are not aligned with each other and power and capabilities are not consonant with threat level. So, countries could not be able to face with the threats in each of its components, as expected.
Civil defense to avoid getting into financial damages or injuries or to minimize the damage caused by the attacks without the use of any weapons and munitions consist wide range of measures. Their performances are possible with low-cost and only parts of it require relatively high costs.
Iran, because of several reasons including its geopolitical situations, having underground rich in oil and mining resources, having high population density and rich history is under threatening. Because of enemies’ high tech and dynamics of modern technology, it is necessary to have a strategy, doctrine, and comprehensive, coordinated, scientific and cultural executive programs to meet the technical demands. For these reasons, the use of passive defense measures against further damage and decreasing enemy invasion is a fundamental issue.
In recent years with the development of passive defense in the world, extensive studies were carried out in this area. In Iran, because of political and strategically importance and military tensions from other countries, the importance and paying much attention to passive defense was formed in late 2003.
Passive defense measures, in modern asymmetric warfare against hostile attacks and reduce the damage caused by air, land and sea attacks of invasive country are of fundamental issues that its scope comprise all infrastructure and facilities of military services, civilian and political issues, communication, road , ports, airports, and bridges, headquarters and the city's population including people and civil properties.
Municipal assets are the most important things that damage during attack and are of critical parts of the city. City assets can be divided into three general categories including vital arteries, economic assets and activity centers and human resources. Utilities, municipal equipments, road communication, critical buildings can be counted of city's major assets. So any disruption leads to impaired performance and threatening life of the urban population.
Psychological factors also play a role in the invasion and destruction of the spirit of life in cities and towns, economic damages and social destruction that should be considered (Abolhasani, 2005). The role of Psychological factors during city attacks should bve mentioned as it has a main role in social life in cities and infrastructure of a community with each other. For maintaining assets, series of solutions are presented in the form passive defense that will have an important role in the defense of the city.
Defense
From the terminology aspect the word "Padafand (in Persian) =defense" is formed of the word "pad" and "afand". In Persian culture "pad or Paad" is a prefix meaning "against, opposing, following" and when placed before a word makes its meaning to be reversed. The word "afand" means "war or hostility (Dehkhoda Ë› 1972, pp. 47 and 48).
Passive defense
Passive defense refers to the set of actions that does not require application of war wares and with using it, we can prevent vital installations damage, sensitive military and non military centers, and human loses and to decrease the extent of damage or to minimize them. Passive defense privacies include tricks, cover, deception, camouflage, distributing secure fortifications and structures and to announce news.
Principles of passive defense
Passive defense principles consist fundamental and infrastructure actions that can be employed to reduce losses and damages, aims to reduce the ability of systems to identify targets, targeted enemy offensive weapon and to impose more costs to them. Passive defense principles include:
- Select the safe geographic areas of a country
- Determine the optimal scale of population and space activities
- Distribution of the functions with threats and geography
- Choose the optimal scale of spread and economic feasibility
- Small and inexpensive construction and initiative in civil defense
- Parallelism associated support systems
- Retrofitting structures, defenses and securing vital centers
- Positioning of operations
- Crisis defensive management in scenes
- Camouflage
- Destruction of enemy intelligence system
- Coverage with natural terrain
- Coverage in all areas
- Deception, initiative and diversity in all actions
- Protection of critical information systems
- Production of dual structures (barriers)
Passive defense strategy objectives
Strategic objectives of passive defense have the most effective on strategy levels. Such goals can be identified as:
- Increased capacity and inhibition capabilities
- Reduce the start of the invasion and spread of attacks
- Protection of personnel, facilities and national investments during invasions (Passive defense in the Mirror of regulations and laws, 2010)
Operational objectives of passive defense
The most important operational goals of passive defense can be described in the form of stages including:
- First, try not to be seen the special centers by enemy hiding, camouflage and tricks (creating false targets)
- Secondly, if being seen by the enemy - not to be known - using coverage and deception aimed at understanding the nature of the goal
- The third step, if being recognized- can not be targeted by the enemy - using natural and artificial factors, using tunnel and etc.
- The fourth stage, if to be targeted- not to be vulnerable or having the least vulnerabilities - using the principles of safety and retrofitting or to be less vulnerable with distribution of critical and sensible parts.
- The Fifth Step, if damage occurs- to quickly rebuild and revive and to sustain an activity – like refurbishing the parts or components and preparing the repairing plans and alternatives (Passive defense in terms of rules and regulations, 2010).
Centers under passive defense
All sensible buildings and critical infrastructure, main arteries of country including all under study, under execution, or exploitation that are suspected to enemy military attacks are divided to
Vital centers
A center that is national in scope and activities and their presence and continued operations is vital for the country. Their capturing or damaging by the enemy cause injury or disorders in the general administration of a country.
Sensible centers
A center that has distributed local activity and its presence or continued operations is necessary for the parts of a country. Their capturing or damaging by the enemy cause disorders in parts of the administration of a country.
Major centers
centers that have a range of local activities. Their presence or continued activities are important for parts of a country. Their presence and disruption by the enemy cause disorders in some parts of a country.
Software methods of passive defense
Software methods refer to methods that do not require specific structures or physical activity but their implementation have important role in success of other ways and even armed defense effectiveness. These methods mainly focus on short, mid and long term planning and sectoral, cross-sectoral, regional and civilian coordination as follows
- Production and training of disaster management programs
- Training the managers and employees
- Production of necessities and guidelines for the use of elements and passive defense techniques at different stages of project studies
- Provide public education to the people in times of crisis
- Paying attention to land use and spatial planning in the defense of vital and sensitive and important centers (Maysami and Mousavi, 2009)
Hardware method of passive defense
Hardware method refers to activities that are required to perform particular physical tasks and includes
- Strong facilities and equipment
- Establishment of shelters
- Use of camouflage techniques (Maysami and Mousavim, 2009)
Active defense
Active defense consists of direct application of nullify in order to neutralize or reduce the effects of air, ground and sea hostilities and destruction on targets. Distinction between passive and active defense is “human factor ". It means that active defense is a tool that needs human user and direct management and consists of war machine and equipments, organizing, training and management of human forces in a way that in the absence of human that instrument itself has no validity. While passive defense is architectural capabilities in the field of war engineering in a way that in the absence of tools, military and combat forces capabilities, and defensive increase. In passive defense the human presence is not required and anyone possesses it, defensive efficiency in war will be increased (Asgharian Jadi, 2007).
Non military defense
In Latin sources the term "non-military defense" or "civil defense" is defined as: non-military defense must "guarantee the safety of the civilian population and their life during war" (Tayari, 1989).
|
|
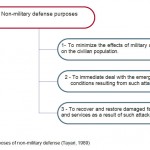
Figure 1: Purposes of non-military |
|
|
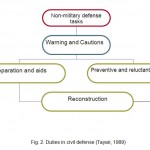
Figure 2: Duties in civil defense (Tayari, 1989) |
Types of threats and risks
Since the beginning of human life, he has grown among risks and has devised various measures to deal with these threats. Some of these threats do not exist, some are new threats and intensity of some threats is more or less. In recent decades the ways to deal with these threats have taken more practical (Asgharian Jadi, 2007).
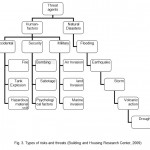
Threats are divided in two categories including natural and man-made. Man-made threats itself are classified in three categories including
- Military
- Security
- accidental.
|
|
Figure 3: Types of risks and threats (Building |
Threat of military invasion includes air, land and sea invasions. Security threats include terrorist bombings and so on. Accidental threats include fires or spills of hazardous materials and explosion of the fuel tanks. (Building and Housing Research Center, 2009).
According to two theorists of third world,Chang Iinmoon and .Edvard Azer, any definition of national security threats depends on several critical values of the community. So, the natures of the threats have different nature according to their issue, from one country to another, and time (Department of National Defense Writers Group, 2008).
In military threats, large parts of risks are about city, its available facilities and equipment. Aside from the cities that physically are great and fix targets and can be targeted even from a distance contract. Either offensive or unwelcome demands, threats are associated with human life and it seems that in many cases there is no escape from it.
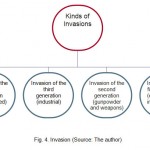
Humanity in the history of 5000 years of civilization on planet Earth has seen approximately 14,000 invasive, resulting in more than four billion people death. At this time only 268 years was without invasion and conflict and it is strange that most invasions in third world countries have occurred (Passive defense in the Mirror of regulations and laws, 2010). Invasion whether wanted or unwanted is interwoven with human life, and it seems that in many cases there is no escape from it.
|
|
Figure 4: Invasion (Source: The author) |
Comparison of the invasion crisis and the crisis caused by natural disasters
There are certain features in the crisis caused by the invasion, which distinguishes them from the crisis caused by natural disasters. These include the following components
- The natures of the threats are constant in natural disasters; just their severity and intensity will change. But in invasions, the natures of threats are flowing and beside of its severity and size, its direction and nature is highly variable.
- In natural disasters such as earthquakes, there is the possibility of different prediction regarding to return periods or floods, droughts and storms, but in invasions, forecasts are strongly influenced by the invasion of foreign agents.
- In the event of natural disasters, the time of accident is limit (a few seconds to a few days in earthquakes, and storms and floods, respectively). In the case of proper organization after event, we can begin actions. But the time of accident even in the short time invasions, is longer than natural disasters and many actions are not possible during the attack.
- After natural disasters the amounts of damages usually fix. But in invasion, after finishing the incident the amount of damages including failed Explosives and so on may be increased.
- In the ways to reduce natural threats, there is no classified information and information about it can be easily exchanged. But in threats, information about attack and ways to deal with it is highly classified, and access and exchange of them is difficult.
- In natural disasters, losses are not for specific targets and occur in a range of natural geography but in the invading, specific goals of cities and infrastructure are under attack.
- In invasions, the enemy goals are determined exactly based on priorities and in terms of how much influence in governance but in natural disasters such factors does not happen.
- In natural disasters, public fears of before occurring the event is less definable, but in invasions due to enemy psychological operations, usually fears will prevail on whole community. In invasions, the enemy's psychological warfare before strike lead to fear, general horror and spirit of popular resistance.
The main fundamental difference in the ways of preventing and reducing the effects of natural disasters, and invasions
Examples of methods for the prevention and mitigation in natural disasters include retrofitting buildings against earthquake faults, avoid of creating buildings and facilities in stuck and Flood retention, protection of vegetation to reduce flood risk and instructions for construction of new and resistant buildings.
Prevention and mitigation measures that can be effective in reducing the attacks of the enemy's ability include to detect such camouflage, hiding, tricks, nationwide distribution, using natural and secure geography, use of resistance facilities and buildings, use of elevation, shelters and principles and criteria of passive defense in development plans (center of logistic and engineering studies and researches, 2007).
Similarities between crises caused by natural disasters, and invasions
- The need to mobilize the resources and capacity to overcome and manage the crisis situations (organizing emergency).
- Create a refugee camp
- Need to aid operations for victims
- Damage caused by the psychological stress of killed and wounded people.
- The need to establish peace and public safety
- The need for special measures to avoid disappointing and defeat sense (Building research center and housing, 2009).
To determine the rate of city vulnerability based on body index The city structure
Spatial distribution of elements, main compounds, functions and elements that make up the city's structure play an important role in the extent of the damage in response to various events, especially military enemy. Physical divisions of the city such as dormitories, neighborhood, district, region, single- core or multi- core are other elements of city structures. Each event has its own talent. For example, in single core structure of the city, economic and human resources focusing on one part of the city in comparison to multi core cities have more vulnerability possibility. While the fall of the city, needs less time, too (Abolhasani, 2009).
Raster cities such as Tokyo, Barcelona, or to some extent, Tehran, due to diffraction of new streets and alleys, necessities to stop in red lights, and crossroads during attacks have not very good defense. So, the best street and passageway plans for defending of citizens against novel wars are star like or radial cities that have provided the nearest residences from cities for the citizens. The more the number of united origins streets, the more choice for running away of non military population will be provided. With the possibility of reducing the traffic congestion, the concentration of population that is always good for the enemy, will be solved. Especially, when such lines usually are of road ways and the primary and main targets of enemy (Ayatollahi, 2009). Given the above information, the approach of passive defense, the most favorable structure for the city is structure of the central institutions that each center is connected to its environment in a radius shape
Tissue of the city
Every tissue of the town or its shape, its size, and how the smallest constituents of the city are, have effective role against military invasions and other city disasters (Abolhasani, 2009). City texture can be studied in the context of different index including
Regular and irregular texture
It can be said that regular and irregular texture, depending on the threat, have different vulnerabilities. For example, in military attacks time, regular textures has better escape possibility and seek relief but irregular texture in military invasion has better act and resistance and because of irregular texture, the possibility programming and organized strikes in anonymous neighborhoods will be less. While residents using irregularities texture, vote for the situation. However, each type of urban texture has direct influence on escape capabilities, take refuge in relief options, aid operations and how to clean up and temporary accommodation (Abolhasani, 2009).
Fine-grained and coarse-grained texture
In fine grained pieces, because of open space and a safe refuge to escape are very low and in crises human death may rise. Generally, the larger the size, the more reduction in human damages and the more temporary accommodation can be more easily done.
Dense and sparse texture
Density indicates the position and kind of a place. Dense and compact texture is an indicator for a complex. It can be said about population and building density, that the less density, the more reduction in texture vulnerability will occur and the enemy will damage by additional expenses in order to act damages.
The rate of filled and blanked spaces
In cities because of high cost of landscape and limitation of constructible places regarding limitation of physical development of cities, filled spaces are larger than empty places. Areas where the built surfaces in comparison to open places are medium or low, due to the better possibility of aid operations after destruction or damage, running and passing from area is also easier and take less damages (Abolhasani, 2009).
Effect of Invasions on infrastructures
Invasion of enemies to infrastructure can be in different ways including blockade, occupation or air invasion of infrastructure. These invasions cause public and special effects to infrastructures.
General and specific effects of the invasions to country's infrastructure can be categorized into following types Socio-economic impacts associated with production discontinuity and delivery of services in infrastructures
The absence of an active and vital installations in industrial manpower due to fear of attacks by the enemy's attacks to vital centers and cities, reduction in raw material input to the industries and disorders in major production process after enemy attack prevent the continued production and service centers in infrastructures. Examples of socio-economic effects resulting from the lack of continuity and services in infrastructure includes following
- Power outage in installations and cities
- Water blackout
- Fuel blackout (gas, oil, gasoline and diesel)
- Disable of air, ground to ground and beach to the sea defense
- Disordering the military and political decision centers
- Disconnection of telecommunications
- Disconnection of notifying information and Broadcasting to people and severe developing rumors
- Interruption of radar controller and more easily attack of enemy to different parts of the country
- Cut the economic activity in banks and capital markets
- Disability of airport, other intra-city and international transportation system such as airports, railway, subway and shipping
- Reducing health centers services like hospitals, the emergencies, and blood Transfusion organization
- Severe shortage of medicines and medical equipments
- Incidence and spread of communicable diseases and poor performance of health- and public and private pharmaceutical centers in non-communicable disease control
- Food shortages and a rise of speculation and overcharging and at the end food shortages (Shakibamanesh and Hashemi Fesharaki, 2009).
Impacts of direct invading of enemy to infrastructures (the scene)
After invasion of the enemy to country infrastructures and facilities some accidents will create in the place of enemy's offensive weapons that can be included as
- Fire
- Killing and wounding of people
- Disconnection of road to infrastructure and crippling of transport system
- Disconnection of telecommunication
- Water, power and fuel blackout to infrastructures
- Blackout the production process due to lack of support resources the underlying injuries and engineering
- Release of chemical hazardous materials, biological or nuclear weapons in the region
- The extreme insecurity in and around infrastructure
- Spreading rumors because of the lack of sufficient announcement
- The enemy act regarding magnification of the incident and make psychological warfare in the country with advertising and media
- Spread of spying in the region by enemy for acquisition of detailed information of attacked centers using internal and International agents and organization
Effects of invasions to towns and villages
The military attack to cities can be by air, land (surrounded and captured town) or sea. Following the invasion of the enemy, the consequences and effects that may occur in towns and villages include
- Destruction of the main decision centers of including political governors, municipal, county
- Discontinued operations in command and control of military or police centers
- Spread of insecurity and increased activity of bandits and robbers in attacks to banks, stores, food and weapon stores, homes and other attractive places
- Lack of control over the population and the influx of people to the output and centers providing facility and services
- Injuring and killing of people after rocketing or fighting face to face with the enemy
- Stop sending food, medicine, blood and Medical equipment
- Spread communicable disease
- Lack of access to primarily health care services in private and public centers
- Disability of inter and intra transportation system of the city including bus, subway, trains and plane
- Major and minor fire
- Blackout of water and occurring drinking water pollution
- Power disconnection
- Off gas and other fuels.
Summarizing and presenting solutions Importance of passive defense
As mentioned above, passive defense is one of the most effective ways to defend against threats and is crucial for most countries. Even in countries like United states and Soviet with high and top military power pay special attention to this subject. In our country, because of its specific geopolitical importance, the vast oil and gas wealth, entering to new field of technologies, the importance of passive defense will be revealed. War years experience in reducing vulnerability and increasing resilience is a witness and the recent invasion also shows its necessities.
|
|
Figure 5: Duties and capabilities of |
Result
War is one of the enduring elements of human history. So, sociologists have introduced it as reality and social phenomenon. Throughout the history of human civilization on Earth, has witnessed numerous incursions that many people have died as a result. Nowadays, the countries that have encountered damages caused by the war, in order to maintain national and vital resources, have given special attention to passive defense.
Passive defense measures in today's asymmetric warfare against the enemy invading and to reduce hostile air attacks and damage caused by ground and sea invasive is fundamental and its dimension cover all urban and regional assess including infrastructures, vital and sensitive military and non-military centers, critical communications such as roads, bridges, ports, airports, and headquarters of the country's population.
Passive defense because of its enhanced role of deterrence can have a large role in reducing the risk of military conflict and beginning a destructive invasion and in the case of correct implementation can reduce the ahead damages.
Passive defense implementation has methods and the solutions that based on them destroying during crises will be the least. One of this ways is to strengthen and reduce the vulnerability of critical assets of cities in crisis based on the principles of passive defense. Among the city's assets, structures and infrastructures, the role of infrastructures as vital arteries of the city is very colorful.
References
-
Ayatollahi Alireza, 2009. Proceedings of passive defense website. Defend of cities against novel wars (in Persian).
-
Asgharian Jedi Ahmad, 2007. Architectural requirements in unsustainable defense of Tehran, Shahid Beheshti University Publications Center.
-
Akbari Abbas, 2006. Passive defense- Introduction to land use planning and defending of Tehran: Deputy of passive defense Air Defense Base of Khatamolanbia, issue no.7.
-
Baghdadi Arash, 2012. Identification of range of municipal assets and presenting them in terms of positioning model in the case of passive defense. Malek Ashtar University, Tehran.
-
Bolhasani Abdollah, 2005. Passive defense- Architecture and Urban Design in Iran. Tehran: Deputy of passive defense of Air Defense Base of Khatamolanbia. Issue no 4.
-
passive defense in the mirror of laws and regulations. 2010.
-
Dehkhoda Ali Akbar. 1972. Dehkhoda wordbook. Volume no 4. Institute of Tehran University publication. pp. 47 and 48.
-
Building and housing research center, 2009. Draft of twenty-first issue, national building regulations.
-
Maysami Hossein, and Mousavi Pedram, 2009. Fundamentals and principles of passive defense. Tehran: Publication of development organization.
-
Advisory.Service on International Humanitarian Law ,2002,Civil Defence in International Humanitarian Law [online]. International Committee of the RedCross,Available from:http://www.icdo.org[Accessed 25 August 2009].
-
Amanda.j.d.,2004,American Civil Security :The U.S.Public and Homeland Security,[online]. Available from:http://www.paydarymelli.ir[Accessed 8 May 2010]
-
Hokkaido Government,2006, Hokkaido Civil Protection Plan[online].Bureau of Crisis Management,Department of General Aff airs, Hokkaido, Available from:http://www.kokuminhogo .go.jp/[Accessed 13 June 2010].
-
Ministry of Housing and urbanism, technical assistant executive center of safe, passive defense in 31 countries, translated by Hamid Tayari, 1989.
-
Center of Logistics Engineering studies and Researches. 2007. Records of experiences of passive defense in the history, Tehran, passive defense Supplement, September 2007.
-
Shakibamanesh, Amir., Hashemi Fesharaki, Seyed Javad. 2009. Passive defense considerations in urban infrastructure. Proceedings of the First Conference on Infrastructure Management, Technical Campus Faculty of Tehran University, November 2009.